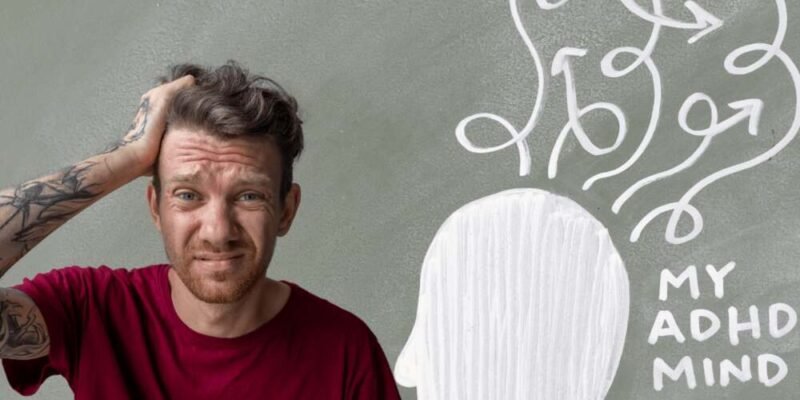
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is often associated with children, but it’s essential to recognize that many adults also live with this condition. The challenges of ADHD do not simply disappear with age; instead, they evolve, creating unique obstacles in adult life. From maintaining focus at work to managing personal relationships, adults with ADHD frequently navigate a complex mental landscape. Understanding and managing ADHD in adults is crucial for improving overall well-being and mental health.
Recognizing ADHD in Adults
ADHD in adults is often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed because its symptoms can be mistaken for other mental health issues, such as anxiety or depression. However, ADHD has distinct characteristics that differentiate it from these conditions. For example, adults with ADHD might experience chronic lateness, an inability to complete tasks, impulsiveness, and difficulty focusing on one thing at a time. These symptoms can lead to significant stress and frustration, particularly when balancing work, family, and social life.
Unlike children, who may display more obvious signs like hyperactivity, adults with ADHD often exhibit less visible symptoms. For instance, they may struggle with disorganization, losing essential items, or forgetting appointments. They may also have difficulty prioritizing tasks, leading to missed deadlines and poor performance at work. These challenges can contribute to a cycle of self-criticism, exacerbating mental health issues.
The Impact of ADHD on Mental Health
ADHD can have a profound impact on an adult’s mental health. The constant struggle to stay organized, meet deadlines, and maintain focus can lead to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem. Many adults with ADHD also experience anxiety as they worry about their ability to meet the demands of daily life. This anxiety can become overwhelming, leading to avoidance behaviors that further complicate their lives.
Additionally, the impulsive nature of ADHD can result in risky behaviors, such as reckless driving or financial irresponsibility, which can lead to severe consequences. The combination of these factors can create a perfect storm of mental health issues, making it essential for individuals to seek proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing ADHD in adults can be challenging because the symptoms often overlap with other mental health conditions. However, a thorough evaluation by a mental health professional, including a detailed personal history and behavior assessment, can help differentiate ADHD from other disorders.
Once diagnosed, adults with ADHD can explore various treatment options. Medication is often the first line of defense, with stimulants like Adderall and non-stimulants like Strattera being commonly prescribed. These medications can help improve focus and reduce impulsivity, but they are not a cure-all. Individuals need to work closely with their healthcare provider to find the proper dosage and type of medication that works best for them.
In addition to medication, therapy can be an effective tool in managing ADHD. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is particularly beneficial as it helps individuals develop coping strategies to deal with their symptoms. For example, CBT can teach organizational skills, time management techniques, and methods for improving focus. Group therapy can also provide support and encouragement from others who understand the challenges of living with ADHD.
Lifestyle Changes and Coping Strategies
While medication and therapy are crucial, lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing ADHD. Regular exercise, for instance, has been shown to help improve focus and reduce hyperactivity in adults with ADHD. Physical activity increases the production of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which are often deficient in individuals with ADHD.
Another effective strategy is creating a structured environment. Adults with ADHD often benefit from routines that provide predictability and help reduce the chaos in their lives. This might include setting regular times for meals, exercise, and sleep, as well as using planners or apps to keep track of appointments and deadlines.
Mindfulness meditation is another powerful tool for managing ADHD. Mindfulness practices teach individuals to focus on the present moment, which can help reduce the mind’s tendency to wander. This practice can improve concentration and reduce the stress and anxiety that often accompany ADHD.
Building a Support System
Having a solid support system is essential for adults with ADHD. Friends, family members, and colleagues can provide understanding and encouragement, helping to mitigate the feelings of isolation that often accompany mental health challenges. Open communication with loved ones about difficulties can foster empathy and create a supportive environment.
Support groups, whether in person or online, can also be incredibly beneficial. Connecting with others who share similar experiences provides a sense of community and belonging, which can be exceptionally comforting for those struggling with ADHD. These groups often share practical tips and coping strategies that have worked for others, offering hope and inspiration.
Do Read: Understanding the Network: HMO, PPO, and Other Medicare Advantage Plan Types