Arthritis is a common ailment that affects millions globally, with knee arthritis being a prevalent type that significantly hinders daily life. If you or someone you know struggles with knee arthritis, understanding treatment options can make a difference. This post will explore practical treatments and tips to help you manage knee arthritis effectively.
What Is Knee Arthritis?
Knee arthritis is a broad term encompassing various forms of joint inflammation that specifically affect the knee. This condition leads to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. The most common type is osteoarthritis, which gradually wears away joint cartilage. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation in the knee joint lining. Both forms can disrupt daily activities, making understanding and managing the symptoms necessary.
Knee arthritis can develop slowly, often starting with minor discomfort. Over time, it may progress to significant pain and mobility issues. Identifying early symptoms is crucial for effective management. Pain when walking, stiffness after sitting, or swelling around the knee are all common indicators.
Understanding the underlying causes is essential. Age, weight, previous injuries, and genetics can contribute to the onset of knee arthritis. Individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition by recognizing these elements.
Recognizing Symptoms of Knee Arthritis
Symptoms of knee arthritis vary but often include pain, swelling, and stiffness. These symptoms can persist or fluctuate, sometimes worsening with physical activity or weather changes. Early recognition is vital for effective treatment.
Pain is typically the most prominent symptom. It may be dull or sharp and is often felt more during movement or after prolonged rest. Swelling occurs due to inflammation and increased synovial fluid in the joint. This can make the knee feel warm and appear more prominent than usual.
Another common sign is stiffness, particularly in the morning or after sitting for long periods. This stiffness can limit the range of motion, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to better management and improved quality of life.
Causes of Knee Arthritis
Several factors contribute to the development of knee arthritis. Aging is a significant factor, as joint cartilage naturally wears down over time. Obesity adds extra stress to the knees, accelerating cartilage breakdown and increasing the risk of arthritis.
Previous knee injuries, such as fractures or ligament tears, can predispose individuals to arthritis. These injuries can alter joint mechanics, leading to increased wear and tear. Genetics play a role, too; a family history of arthritis can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
Inflammation from autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis can directly cause knee arthritis. Understanding these causes helps craft personalized treatment plans that address individual risk factors.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Diagnosing knee arthritis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. Your physician will inquire about symptoms, their duration, and any history of knee injury.
During a physical exam, the doctor will assess the knee’s range of motion, swelling, and pain points. Imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs provide detailed views of the joint, highlighting cartilage loss, bone changes, and other abnormalities.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. Early identification allows for interventions that can slow disease progression and improve quality of life.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of defense against knee arthritis. These include lifestyle changes, physical therapy, and medications that reduce symptoms and improve joint function.
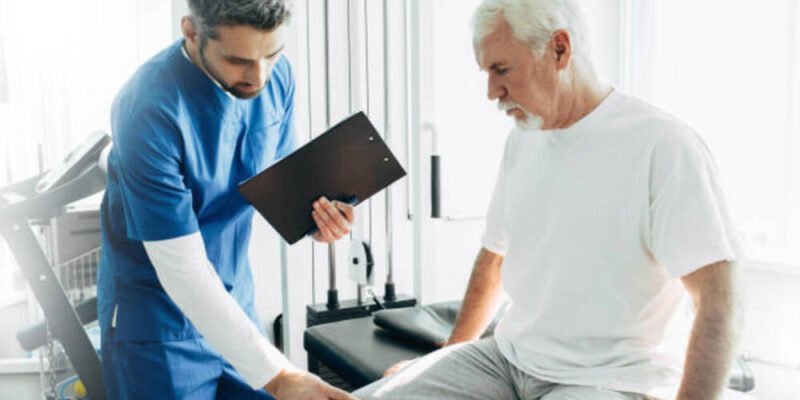
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing knee arthritis treatment in Houston. A physical therapist can design exercises to strengthen muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and enhance mobility. Regular exercise combined with appropriate rest can significantly reduce symptoms.
Medications such as NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) help manage pain and inflammation. Depending on the severity of symptoms, they are available both over-the-counter and by prescription. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any medication regimen.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Management
Lifestyle changes are integral to managing knee arthritis effectively. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces knee stress and can slow arthritis progression. Every pound lost can significantly decrease the load on your knees.
Incorporating low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling can improve joint health without exacerbating symptoms. These activities keep the knee mobile and strengthen supporting muscles, enhancing stability and function.
The diet also plays a role in managing arthritis. Consuming anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3-rich fish can help reduce joint inflammation. Staying hydrated and avoiding excessive alcohol and sugar intake are also beneficial.
Advanced Treatment Modalities
Advanced treatments may be necessary when conservative measures don’t provide adequate relief. These include injections, bracing, and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections, administered directly into the knee joint, can temporarily relieve pain and inflammation and offer months of symptom relief.
Braces support the knee, providing stability and reducing pain during movement. They can correct joint alignment and distribute weight more evenly across the knee joint. Surgery is considered when other treatments fail to alleviate pain and disability. Options range from arthroscopic procedures to partial or total knee replacements.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery becomes an option when knee arthritis severely impacts the quality of life, and other treatments are ineffective. Procedures vary based on the severity and type of arthritis.
Arthroscopy involves inserting a small camera into the knee joint to remove loose cartilage or repair torn tissue. This minimally invasive technique can relieve symptoms and improve joint function.
Partial knee replacement focuses on replacing only the damaged portion of the knee, preserving as much of the natural joint as possible. Total knee replacement involves replacing the entire knee joint with artificial components, offering significant pain relief and restoring mobility.
Importance of a Personalized Treatment Plan
Each individual’s experience with knee arthritis is unique, necessitating a personalized treatment approach. Collaborating with healthcare providers allows for tailored plans that address specific symptoms and lifestyle needs.
A comprehensive plan may include a combination of physical therapy, medications, lifestyle changes, and advanced treatments. Regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals ensure the plan remains effective and adjustments are made as needed.
Empowering patients to understand their condition and treatment options can improve adherence and outcomes. Education about knee arthritis fosters proactive management and improves overall health and well-being.
Living with Knee Arthritis
Learning to live with knee arthritis involves managing symptoms and maintaining a fulfilling lifestyle. While the condition poses challenges, many strategies exist to enhance daily living and reduce discomfort.
Assistive devices like canes or walkers can aid mobility and decrease pain during activities. These tools provide support and stability, making it easier to perform tasks independently.
Engaging in social and recreational activities is essential for mental well-being. Finding hobbies that accommodate physical limitations, such as gardening or painting, can provide joy and a sense of accomplishment.
Support and Resources
Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends plays a crucial role in managing knee arthritis. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide encouragement and practical advice.
Support groups and online communities offer platforms for sharing stories, tips, and resources. These networks foster a sense of belonging and provide valuable insights into living with arthritis.
Access to reliable information and resources is essential for informed decision-making. Organizations like the Arthritis Foundation offer educational materials, workshops, and support services to empower individuals with arthritis.
Conclusion
Knee arthritis is a manageable condition with the right approach and resources. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take control of their health and improve their quality of life.
While knee arthritis may require adjustments, many strategies can enhance well-being and reduce symptoms. Collaborating with healthcare professionals and staying informed empower individuals to manage their condition effectively.
For those seeking additional support and guidance, reaching out to healthcare providers and accessing reliable resources is a valuable step. Together, we can take the healing steps necessary to manage knee arthritis and live life fully.
Also read interesting articles at Disboard.co.uk